Insect fishing nozzle
 In nature, there are countless insects, of which a significant part in one or another phase of development can be used as a good nozzle when fishing. This review includes only some species of insects that have been tested as a bait by the experience of many anglers and are found in large numbers.
In nature, there are countless insects, of which a significant part in one or another phase of development can be used as a good nozzle when fishing. This review includes only some species of insects that have been tested as a bait by the experience of many anglers and are found in large numbers.
Fisherman, in addition to the name of insects, it is useful to get acquainted with their biological nature, with the development of the insect during the entire life cycle. This will allow you to know the time and methods of extraction and use of not only the species described in the review, but also other insects useful in fishing.
Upon completion of development in the egg, i.e. the embryonic phase, hatching occurs; from this point on, the insect enters the second stage of its development – the larva phase, from which the post-embryonic, or postembryonic, period begins. In this phase of development, the growth of the larvae is accompanied by periodic molts – throwing off the old skin. The next phase of transformation of the larva is an adult phase, called imago.
In the first case, the transition to an adult insect takes place directly from the larva with the last molt; in the second case, through a special intermediate phase of development, the pupa. In accordance with this, three are typical of the first and four phases of the second. The number of periodic molts in the process of growth of the larvae varies among different groups and species of insects, varying from 3 (flies) to 4-6 (locusts, butterflies) and even up to 45 (mayflies). Adult insect – imago is the final phase of the life cycle. But not always the transition to this phase completes the development (to the mature state) of the individual.
The life cycle takes place in different insect species at different times. Some species have one generation in a year, others – 2-3 or more generations, others during the year pass only part of the development cycle and they need 2-3 years or more to complete the generation.
For fishers, almost all insects are of interest mainly in two phases of development – the larva phase and the adult insect phase.
Dragonfly fishing
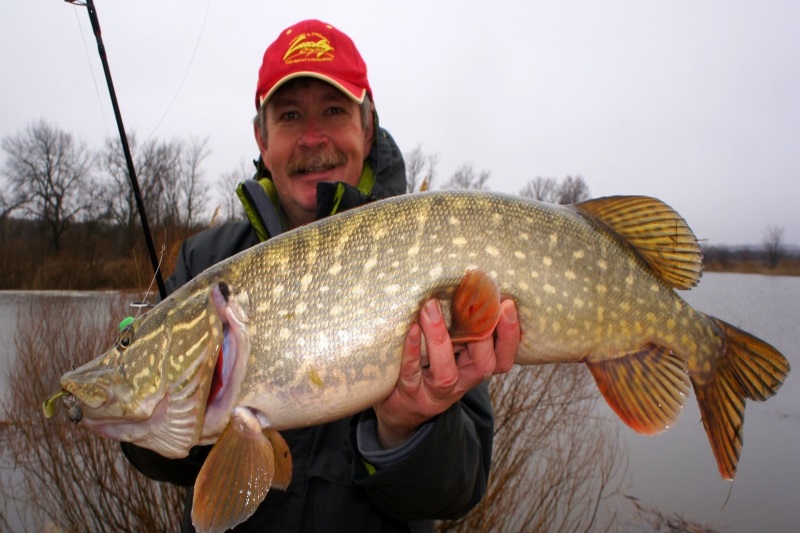
In nature, there are thousands of species of dragonflies. Only in the territory of the Russian Federation – about two hundred species and in the European part – 65. Large dragonflies and their larvae – a dragonfly-yoke (Aeschna genus, Aeschnidae family) and a flat dragonfly (such as Libellula quadrimaculata) are of the greatest interest in fishing. Flight dragonflies are used for fishing with fly fishing of chub, ide, trout, grayling, asp and other fish. Most used flat dragonflies with a thick body. When the nozzle hook stuck in the torso to the very throat, pass it through the torso. Sometimes the wings tear off completely or cut off by half. Hooks apply the number 8 and 10 for the European numbering.
Dragonfly larva is an excellent nozzle when fishing for large fish – bream, carp, perch and many others.
Larvae of most species of dragonflies develop in fresh, non-flowing or low-flow water bodies with a silt bottom and rich aquatic vegetation. A prerequisite for the development of larvae is the abundance of food of animal origin (dragonfly larvae and flying dragonflies are predators). In pure reservoirs, as well as in rivers with clean shores, dragonfly larvae have very little or none at all.
Almost all dragonflies winter in the larval phase. The development of the larvae of many species of large dragonflies, depending on the climate and feeding conditions, lasts two or even three years. During this period, they molt from 7 to 11 times. At first, the larva has a size of 1-2 mm, and by the time it becomes an insect, the nymph stage reaches 4 cm or more. At this stage, they begin to breathe atmospheric air and, on any support — the plant stalk, pile, stone — crawl out half of the water and remain in that position from several hours to several days. After that, the larva rises above the support or crawls to the shore, where it sits motionless for half an hour, and then it is released from the skin. Dragonfly larva for fishing
In the dragonflies that have just appeared, the wings are soft, with careless movement they are easily deformed, but quickly acquire stable rigidity. After 2-4 hours, the dragonfly begins to fly. In the middle band, mass flights of dragonflies are observed when the night temperature stably keeps at a level not lower than 10 degrees Celsius. Most often this occurs in mid-June. More species live in the south, and flights take place throughout the summer. Moreover, the flights of dragonflies of one species occur almost simultaneously within 2-3 days. Sometimes during this period you can see a lot of discarded larvae in the coastal strip – it means that the flight has already passed.
Gathering the larvae for fishing is necessary at a time when they are just beginning to emerge from the water, and only along the banks lit by the sun, in places where there is a lot of coastal vegetation – reeds, sedges or willow thickets. It is even better to catch them in the spring before the mass departure, when the water warms up a little, using a small nonsense.